Introduction
A. Introducing Caches
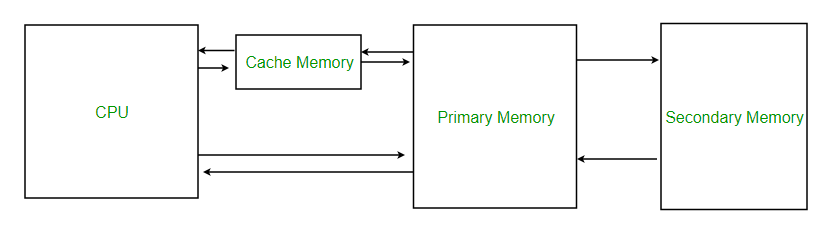
Cache memory, or cache, is a type of high-speed memory. It stores frequently accessed data temporarily. Central processing units (CPUs), web browsers, applications, and operating systems use caches as hardware and software components.
B. Caches in Computer Systems
The CPU processes tasks and executes instructions in a computer system. It requires data originally stored in the system's memory components to perform tasks. As for the main memory (random access memory, RAM), it acts as the primary storage unit. Modern CPUs are advanced such that it usually takes more time to retrieve data from the main memory than performing the tasks themselves. Hence, the CPU usually remains idle while waiting for the data, causing performance bottlenecks which lower the efficiency of operations with the CPU. The CPU cache acts as a temporary high-speed data storing unit between the CPU and the main memory to accelerate data retrieval and input-output operations.
By Cheng Man Ho (56612619)
Click to view the source code of this page.